cervical compression test thoracic outlet syndrome|thoracic outlet syndrome mri results : distributor Thoracic outlet syndrome is a neurovascular disorder resulting from compression of the brachial plexus and/or subclavian vessels in the interval between the neck and axilla. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with .
28 de nov. de 2022 · O próximo jogo do Brasil na Copa do Mundo vai acontecer no dia 5 de dezembro, às 16h (de Brasília). Classificada em primeiro lugar no Grupo G, a Seleção vai enfrentar a Coreia do Sul nas oitavas de final da competição, no estádio 974. A partir das oitavas e final, os jogos da Copa do Mundo são de caráter eliminatório.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Feel free to post any comments about this torrent, including links to Subtitle, samples, screenshots, or any other relevant information. Watch The Punisher Season 1 (S01) Complete 1080p DD5 1 - 2 0 x264 Phun Full Movie Online Free, Like 123Movies, FMovies, Putlocker, Netflix or Direct Download .
ultrasound for thoracic outlet syndrome
The first narrowing area is the most proximal and is named the interscalene triangle: This triangle is bordered by the anterior scalene muscle anteriorly, the middle scalene muscle posteriorly, and. See moreSigns and symptoms of thoracic outlet syndrome vary from patient to patient due to the location of the nerve and/or vessel involvement. Symptoms range from mild pain and sensory changes to limb-threatening complications in severe cases. 1. Patients with thoracic outlet syndrome will most likely present pain anywhere between the . See moreDue to its variability, TOS can be difficult to distinguish from other pathologies with similar presentations. A thorough history and evaluation must be done to determine if the patient’s symptoms are truly TOS. The following pathologies are the common differential diagnoses for TOS: 1. Carpal tunnel syndrome 2. De Quervain’s tenosynovitis 3. . See more Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a group of conditions in which there's pressure on blood vessels or nerves in the area between the neck and shoulder. This space is known .
Your healthcare professional does a physical exam to look for signs of thoracic outlet syndrome. These may include a depression in your shoulder or a bony area above the . Thoracic outlet syndrome is a neurovascular disorder resulting from compression of the brachial plexus and/or subclavian vessels in the interval between the neck and axilla. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with .
brix handheld refractometer analyse food
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a nonspecific diagnosis representing many conditions that involve the compression of the neurovascular structures that pass through the . Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) occurs when there’s compression of nerves or blood vessels in your lower neck and upper chest. Symptoms include pain, tingling and .Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a general term used to describe three conditions which occurs in the thoracic outlet, an area formed by the top ribs and the collarbone. The syndrome occurs when a nerve or blood vessel is . Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) may affect neurological or vascular structures, or both, depending on the component of the neurovascular bundle predominantly compressed. Types include neurological, arterial, .
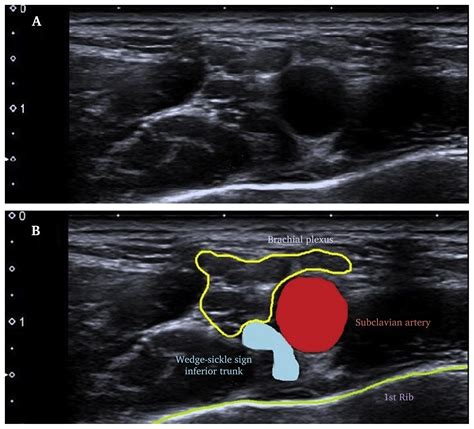
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a term used to describe a group of disorders that occur when there is compression, injury, or irritation of the nerves and/or blood vessels (arteries and . Assessing Cervical Rib Thoracic Outlet Syndrome. The fourth type of thoracic outlet syndrome, cervical rib syndrome, cannot be reliably assessed with orthopedic testing, although it will usually show positive with .
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a nonspecific diagnosis representing many conditions that involve the compression of the neurovascular structures that pass through the thoracic outlet. TOS was first reported by Rogers in 1949 and more precisely characterized by Rob and Standeven in 1958.[1] Wilbourne suggests five different types of TOS; a venous . Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is an umbrella term for conditions involving the compression of neurovascular structures . Pancoast syndrome, cervical disc disorders, fibromyalgia) Other . Neurogenic TOS: electromyography/nerve conduction studies; Venous TOS: duplex ultrasonography; Arterial TOS: MR angiography; Arterial thoracic outlet syndrome (AOTS) is a compressed artery between your ribs and collarbone. . hands, neck and head. The extra cervical rib can compress your subclavian artery, blocking blood flow and allowing blood clots to form. These blood clots may break off and travel through your arm, getting in the way of proper blood flow .Since its inception in 1956 by Peet et al. , thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) has been used to refer to a constellation of symptoms resulting from neurovascular compression at the thoracic outlet, usually resulting in some combination of pain in the neck and upper extremity, weakness, sensory loss, paraesthesias, swelling, and discoloration .
Most patients who have a thoracic outlet compression syndrome without objective neurologic deficits respond to physical therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and low-dose tricyclic antidepressants. If cervical ribs or subclavian artery compression is identified, an experienced specialist should decide whether surgery is necessary.
Thoracic outlet syndrome is a term used for several different conditions that can occur when nerves and/or blood vessels in the thoracic outlet are . Symptoms from nerve compression are much more common than symptoms from blood vessel compression; they are also easier to diagnose. . Doctors often use the elevated arm stress test to help .
Thoracic outlet syndrome, a group of diverse disorders, is a collection of symptoms in the shoulder and upper extremity area that results in pain, numbness, and tingling. . Nerve compression at the cervical spine or elbow and wrist, involving the median and ulnar nerve, may occur in conjunction with TOS. . Gillard J, Pérez-Cousin M .Purpose [edit | edit source]. Adson's test is a provocative test for Thoracic Outlet Syndrome accompanied by compression of the subclavian artery by a cervical rib or tightened anterior and middle scalene muscles.. Technique [edit | edit source]. Starting Position. The test can be performed with the patient in either sitting or standing with their elbow in full extensionCauses of thoracic outlet syndrome. Thoracic outlet syndrome can happen if the nerves or blood vessels running along the top of the rib cage (an area called the thoracic outlet) become squashed. Things that can lead to thoracic outlet syndrome include: being born with an extra rib – this is known as a cervical rib; poor posture; having large .
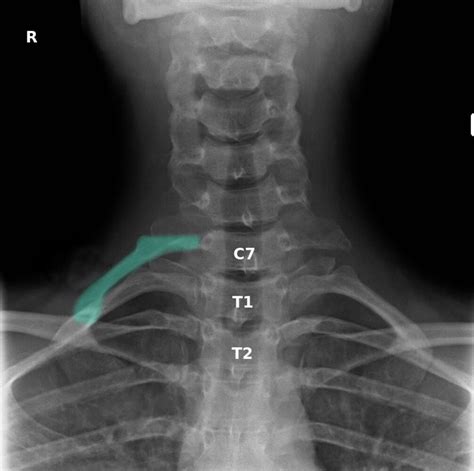
thoracic outlet syndrome x ray
Purpose [edit | edit source]. This test is a diagnostic tool used in the identification of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS).It is also known as the “elevated arm stress test” or "EAST". Clinically Relevant Anatomy [edit | edit source]. Please refer to the Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) page.. Technique [edit | edit source]. Starting postion: The patient has both arms in the 90° .Neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome (nTOS) is a condition involving chronic compression of the brachial plexus. It is the most common of all thoracic outlet syndromes (TOS), accounting for approximately 97% of cases. 1,2 This can result in a spectrum of symptoms from mild pain in the arm and shoulder on excessive use to disabling motor wasting and sensory disturbance at .
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) has been classified as neurogenic (95% of cases), venous (3- 5%), or arterial (1%). . and trigger points that can reproduce the symptoms. The EAST (elevated arm stress test) test involves elevating the arms above the head and opening and closing the fists for 3 minutes. . Loss of the pulse suggests compression .Most patients who have a thoracic outlet compression syndrome without objective neurologic deficits respond to physical therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and low-dose tricyclic antidepressants. If cervical ribs or subclavian artery compression is identified, an experienced specialist should decide whether surgery is necessary.Hyperabduction Test (Wright’s Test) Roos Test OVERVIEW Thoracic outlet syndromes (AKA, cervical rib, scalenus anticus, costoclavicular, hyperabduction and pectoralis minor syndrome) are a group of syndromes primarily associated with arm symptoms. Neurovascular entrapment is thought to be caused by compression of the brachialThoracic outlet syndrome is a variety of symptoms that happen from a narrowing of your thoracic outlet—the space between your collarbone and your first rib. . Symptoms of thoracic outlet syndrome relate to the compression of blood vessels and nerves. Possible symptoms are: . Providers often use a specific test to help diagnose thoracic .
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) describes a pain syndrome of the neck and arm caused by compression of nerves or blood vessels on arm motion. . Diagnostic Tests for Thoracic Outlet Syndrome; . The first rib is often . Thoracic outlet syndrome Intermittent paresthesias, pain worsened by use, unilateral symptoms; may be confused with cervical radiculopathy Positive Roos test, tenderness to palpation over distal .
Arterial TOS is rare and the least frequently encountered thoracic outlet compression disorder; Typically caused by subclavian artery compression in association with a cervical rib or first rib anomaly; . MD, at The Washington University Center for Thoracic Outlet Syndrome at Barnes-Jewish Hospital.) History and symptoms of arterial TOS .
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a condition in which there is compression of the nerves, arteries, or veins in the superior thoracic aperture, the passageway from the lower neck to the armpit, also known as the thoracic outlet. [1] There are three main types: neurogenic, venous, and arterial. [1] The neurogenic type is the most common and presents with pain, weakness, . The term "thoracic outlet syndrome" was coined to collectively encompass the spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet . Distinct terms are used to describe the predominantly affected structure, including neurogenic (nTOS) from brachial plexus compression, venous (vTOS) from subclavian vein compression, and .
The Brachial Plexus Compression Test is not sufficient enough to distinguish between patients with Thoracic Outlet Syndrome and cervical radiculopathy, because the test is probably positive in both cases. Also, due to lack of information on its diagnosis accuracy, it is difficult to take objective stands on its clinical value. What is thoracic outlet syndrome? Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a term that refers to three related syndromes involving compression of the nerves, arteries, and veins in the lower neck and upper chest area. This compression causes pain in the arm, shoulder, and neck. Symptoms of TOS vary depending on the type:What is thoracic outlet syndrome? Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a syndrome that can cause any combination of pain, weakness, numbness, tingling, sensation of coldness or, sometimes, a more general feeling of discomfort in portions of the upper body. It commonly affects in one or both of the upper limbs (arms) and/or the hands, armpits, upper back, neck and .
thoracic outlet syndrome test
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) describes a group of disorders due to compression of the nerves or blood vessels as they pass through the thoracic outlet. Jump to content. Updated visitor policies. Other Michigan Medicine Sites . There is no definitive test to diagnosis NTOS. However, there are tests that are useful to rule out other .
The primary purpose of the Washington University Center for Thoracic Outlet Syndrome at Barnes-Jewish Hospital is to better treat patients. . when Raynaud’s phenomemon or complex regional pain syndrome are suspected, but these tests are rarely performed in current practice. Electrophysiologic tests. . Alignment of the cervical and upper .
Thoracic outlet syndrome refers to a group of conditions caused by compression of the nerves or the blood vessels in the area around the collarbone. The most common type of TOS occurs when the nerves (specifically part of the brachial plexus) are pinched between the collarbone and the first rib.
thoracic outlet syndrome physical exam
08h. 10h. 12h. 14h. 16h. 18h. 20h. 22h. Temperatura. Chuva. Vento.
cervical compression test thoracic outlet syndrome|thoracic outlet syndrome mri results